Which Best Describes the Basic Structure of a Virus
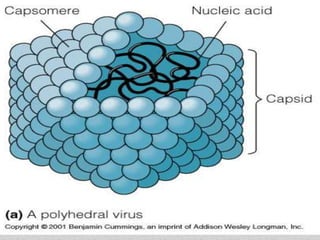
Virus capsids are predominantly one of two shapes helical or icosahedral although a few viruses have a complex architecture. Virion an entire virus particle consisting of an outer protein shell called a capsid and an inner core of nucleic acid either ribonucleic or deoxyribonucleic acid RNA or DNA.
Structure Of Viruses Boundless Microbiology
These computer viruses are present in various types and each of them can infect a device in a different manner.
. After about 20 seconds of contact soap breaks apart the. The source of the envelope is from the membranes of the host cell. They do not have a cellular structure.
Heat breaks the structure of the spike. The core confers infectivity and the capsid provides specificity to the virus. Viruses may be viewed as mobile genetic elements most probably of cellular origin and characterized by.
Characteristics of Life Viruses Quiz. A tail surrounded by a carbohydrate coat. Nucleic acid strand surrounded by a carbohydrate coat.
In other words viruses dont grow and divide. A computer virus is a kind of malicious computer program which when executed replicates itself and inserts its own code. Encapsulating the RNA genome is the viral envelope teal which protects the virus when it is outside of a host cell.
Bound to this string of RNA are nucleoproteins dark blue discsproteins that help give the virus its structure and enable it to replicate. DHerelle introduced the term bacteriophages for these agents and also described the. A tail surrounded by a protein coat.
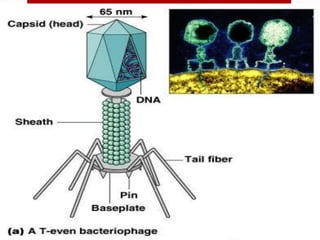
Head- The head consists of 2000 capsomeres with double-stranded DNA enclosed within. Instead new viral components are synthesized and assembled within the infected host cell. Instead they have a core of genetic material surrounded by a.
Which best describes the basic structure of a virus. The notion that viruses were structurally composed of repeating subunits. The genetic material or genome of a virus may consist of single-stranded or double-stranded DNA or RNA and may be linear or circular in form.
RNA-dependent-RNA polymerase or other enzymes -. An icosahedral shape is the most efficient way of creating a hardy structure from multiple copies of a single protein. Which best describes the basic structure of a virus.
When the replication is done this code infects the other files and program present on your system. - All viruses have a protein coat capside or shell that surrounds and protects the nucleic acid core. Viruses may contain either DNA or RNA as their genetic material.
Viral nucleocapsids come in two basic shapes although the overall appearance of a virus can be altered by the presence of an envelope if present. This suggests that potential vaccine and antibody-based treatment strategies will need to be unique to the new virus. - Some viruses package enzymes - eg.
In some virions the capsid is further enveloped by a fatty membrane in which case the virion can be inactivated by. Nucleic acid strand surrounded by a protein coat. They are acellular that is they contain no cytoplasm or cellular organelles.
Viruses are small obligate intracellular parasites which by definition contain either a RNA or DNA genome surrounded by a protective virus-coded protein coat. Ultraviolet light disrupts the genetic material. The IAV genome consists of eight single-stranded viral RNA segments contained in separate viral ribonucleoprotein vRNP complexes that are packaged together into a single virus particle.
This shape is used because it can be built from a single basic unit protein which is used over and over again. Viruses are acellular non-living organisms. Characteristics of Life Viruses.
A basic virus is composed of a genome capsid and viral envelope. This saves space in the viral genome. Adenovirus an icosahedral virus.
Section 22 Structure of Viruses The simplest viruses are composed of a protein capsid that protects the viral nucleic acid from the harsh environment outside the cell. Viruses are only active within host cells which they need to reproduce while bacteria are single-celled organisms that produce their own energy and can reproduce on their own. A tail surrounded by a carbohydrate coat.
Which best describes the basic structure of a virus. Systemic diseases caused by viral infection include influenza measles polio AIDS and COVID-19. The structure of viral RNA is believed to play a role in assembling the different vRNPs into budding virions 1-8 and in directing reassortment between IAVs 9.
A tail surrounded by a protein coat. Nucleic acid strand surrounded by a protein coat. The tail is an often elaborate protein structure.
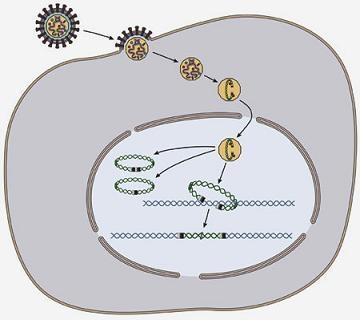
Virus Life Cycles Figure. Computer Virus and its Types. A virus particle is made up of genetic material housed inside a protein shell or capsid.
Nucleic acid strand surrounded by a carbohydrate coat. Helical viruses have an elongated tube-like structure with the capsomers arranged helically around the coiled genome. RNA viruses include HIV and hepatitis C virus.
Despite similarities in sequence and structure between the spikes of the two viruses three different antibodies against the 2002 SARS virus could not successfully bind to the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. A tail surrounded by a carbohydrate coat. They carry out no metabolism on their own and must replicate using the host cells metabolic machinery.
They are classified as obligate intracellular parasites which require a host organism to function. Generalized Replication of Viruses Though the details of virus infection and replication vary greatly with host type all viruses share 6 basic. This outer envelope is made from a layer of lipids a waxy barrier containing fat molecules.
A tail surrounded by a protein coat. - Some viruses have a lipid envelope or membrane surrounding a nucleocapsid core. Frederick Twort and Felix dHerelle working independently are credited with the discovery of viruses which could infect and lyse bacteria in 1915.
Tail- The tail consists of an inner hollow tube which is surrounded by a contractile sheath with 24 annular rings. RNA viruses have an enzyme called reverse transcriptase that permits the usual sequence of DNA-to-RNA to be reversed so that the virus can make a DNA version of itself. Nucleic acid strand surrounded by a protein coat.
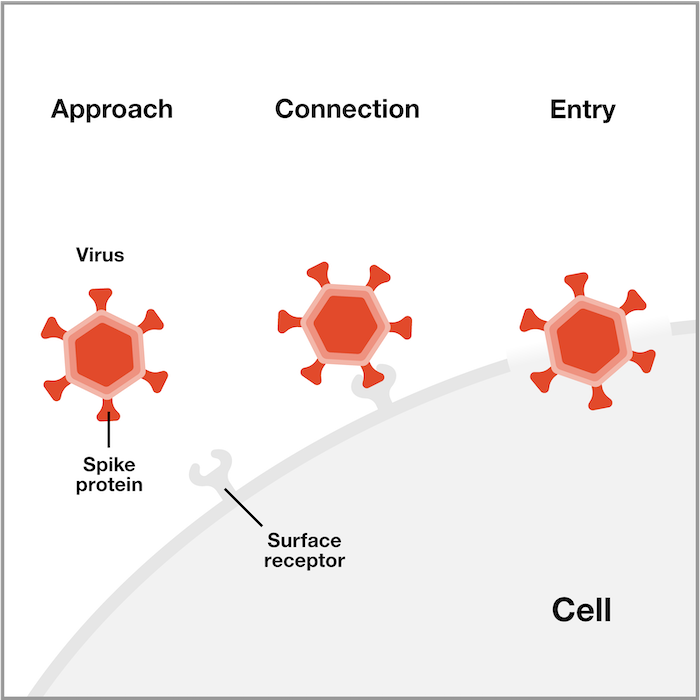
It aids in binding to the surface of the host cell and in the introduction of virus genetic material to the host cell. Bacteria serve many vital roles in nature outside of being infectious. The bacteriophage consists of a polyhedral head a short collar and a helical tail.
Herpes simplex virus and the hepatitis B virus are DNA viruses. Virus particles have a variety of shapes. Nucleic acid strand surrounded by a carbohydrate coat.

What Are Infectious Diseases Facts Yourgenome Org

Dna Vs Rna 5 Key Differences And Comparison Technology Networks
Structure Of Viruses Boundless Microbiology

Ccna 2020 Training In Noida Ccna Institute Train
Viruses Structure Classification And Characteristics

Viral Structure An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Viral Structure An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Viruses Special Issue Retroviral Enzymes

Structure Of Viruses Boundless Microbiology

Structure Of Viruses Boundless Microbiology

Essential Oils 101 Cells Project Cell Parts Biology

Viral Structure An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Viruses Structure Classification And Characteristics

Picture Computer Literacy Lesson Plans Computer Lessons Teaching Computers
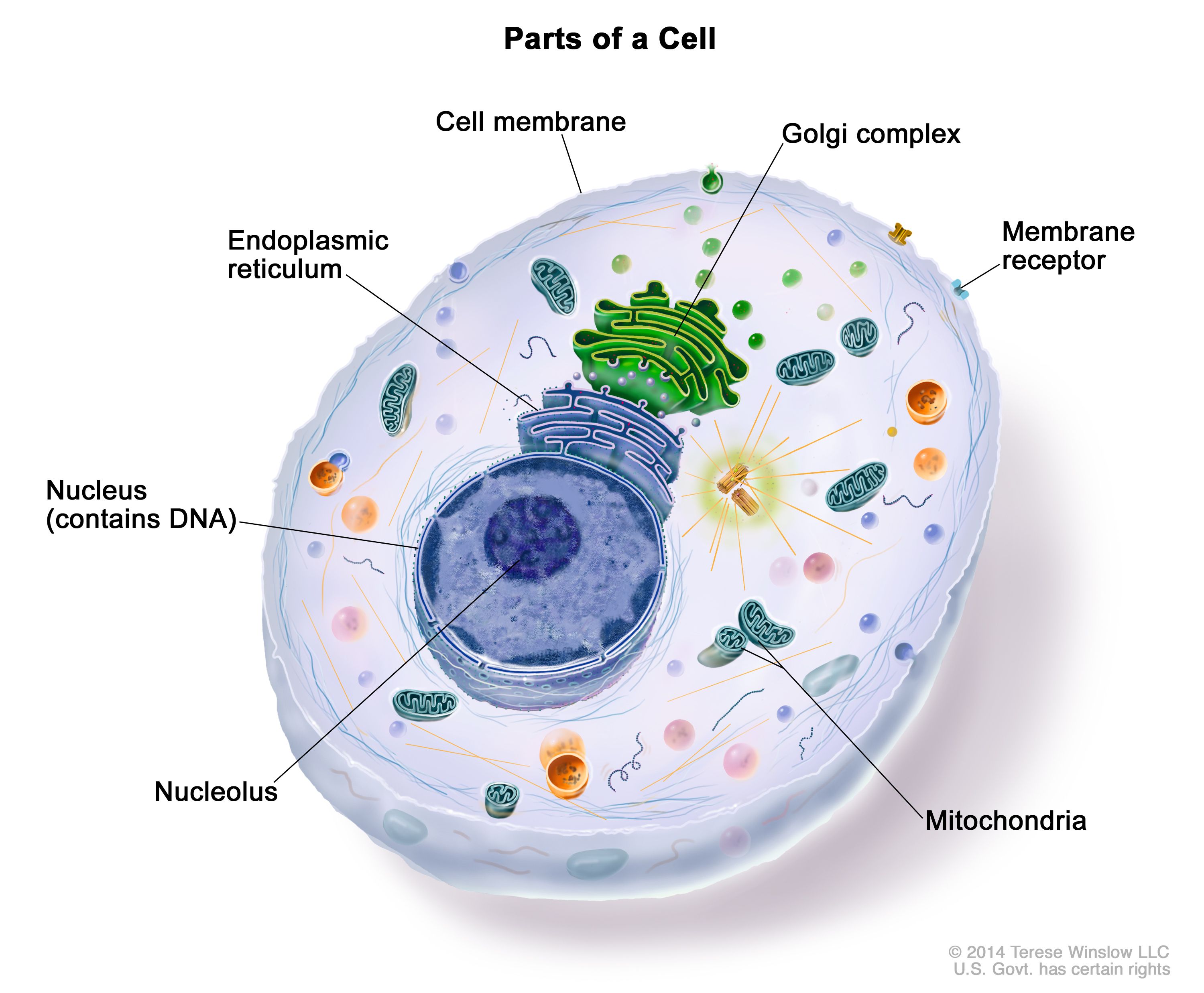
Definition Of Cell Nci Dictionary Of Cancer Terms National Cancer Institute



Comments
Post a Comment